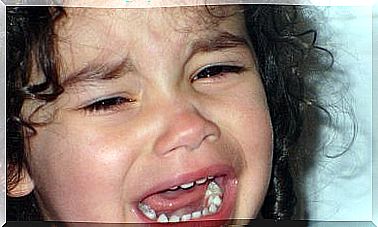
Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy In Children

Did you know that the most common allergy in children is cow’s milk protein allergy? In addition, it is usually one of the first to manifest itself, as cow’s milk is usually introduced before the first year of age and the rest of allergenic foods. This allows its early detection and treatment can be started as soon as possible to avoid risks.
This allergy usually affects 2% of children and tends to persist into adulthood. The most important thing is to differentiate it from lactose intolerance, as the amount of food to be avoided is greater. Therefore, it is advisable that you pay attention and inform the school, especially if your child eats there.
Do you want to know how to detect it and how to act in case of an unexpected reaction? Know what is allowed to eat or how to prepare food to avoid cross-reaction? Stay tuned because we’ll tell you all of this below.

Diagnosis and symptoms of cow’s milk protein allergy
First, this allergy is an immune system response. Therefore, detection is done using IgE antibodies in the blood. That said, there are 2 ways that allow for its assessment, the prick test and the blood test.
On the one hand, the prick test involves injecting the allergen under the skin and observing the appearance of red and itchy blisters over time. In the case of children, this method is the least invasive, which is why it is the most used. On the other hand, the blood test allows you to assess the reaction of blood cells to milk proteins.
Both must be accompanied by a medical history that includes family history, age at onset, and time elapsed between ingestion of the allergen and symptoms.
It usually manifests as itchiness and redness of the skin, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and respiratory pain that appear after a few hours.
dietary treatment
Unlike lactose intolerance, dairy products are not solely responsible for the allergy to cow’s milk protein. Also involved are beef and beef products, such as hamburgers, sausages, cannelloni, among others.
Furthermore, there is a great similarity between the proteins in milk and goat and sheep meat. Therefore, they should be avoided, as well as any source of lactoglobulins and casein.
These can be found in sauces, preserves, processed foods, chocolate, cocoa, cereals, some breads, sausages and sweets, as they are used as additives, and also in soaps, body creams and medicines. Therefore, before buying, read the label carefully or ask the seller for advice, as it is mandatory to specify its presence.
However, traces are exempt because the quantities are very small and, in most cases, their presence is due to cross contamination as there are no different production lines. Therefore, if you are unsure whether a product is free from cow’s milk protein, it is best not to buy it.
Finally, remember to use different utensils between allergen-free foods and others, and prepare them in separate areas to avoid contact. Also, clean all surfaces and dishes thoroughly after use.
Nutritional alternatives for children with cow’s milk protein allergy
With regard to dairy products, you have at your disposal highly hydrolyzed formulas from which the proteins that cause allergies are eliminated. Otherwise, you can resort to vegetable drinks, although the following recommendations must be taken into account:
- It is recommended to introduce the soy drink after 12 months.
- The rice drink is not recommended as it contains large amounts of arsenic, a toxic mineral present in the growing soil.
- Other beverages, such as oats and oilseeds, can be consumed without problems, although their nutritional value is not similar to that of milk, as they have almost no protein and stand out for their high-quality carbohydrate and fat content, respectively.
- Choose those that have no added sugars and, if possible, are fortified with vitamin D and calcium.
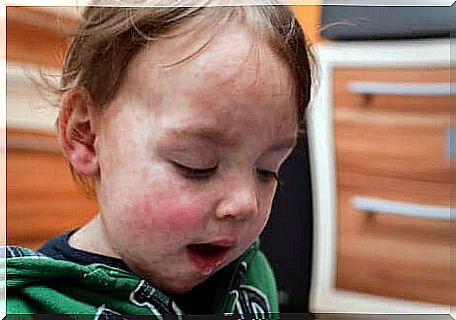
As for meat, you can offer your child chicken, rabbit, turkey and pork, which are softer. Also, if you offer a citrus fruit or pepper at the same meal, it will also improve iron absorption.
Learning to live with cow’s milk protein allergy
After your child is diagnosed with a cow’s milk protein allergy, it’s normal to have many questions like the ones we’ve just resolved. This is because they are foods whose consumption is considered basic, at least that is what is intended considering their role in bone growth and anemia prevention.
However, there are other foods with the same benefits, such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, almonds, beans, shellfish, fish and other meats.
In addition, at the beginning, it is necessary to be careful when shopping or eating out, always informing yourself so that contact and accidental ingestion does not occur. Therefore, always carry adrenaline with you to reduce the impact of an anaphylactic shock , which manifests itself through difficulty breathing, dizziness, sweating and tachycardia, among other symptoms.