What Is The Blood Glucose Curve Test?
Diabetes is a disease known and feared by many people. Its main characteristic is the persistently high concentration of glucose in the blood. This could be the cause of deficient insulin production, an increase in glucose production, body insulin resistance, or a combination of factors.
It is a chronic and degenerative disease, non-communicable and also incurable. However, it can be controlled. People with diabetes can live with this disease for many years. Statistics indicate that approximately 15% of the world’s population suffers from diabetes.
Complications associated with diabetes
This disease is associated with a series of complications in various body systems. For example, vision loss or progressive kidney deterioration may occur.
As well as, in severe cases, there is the possibility of losing one of the lower extremities due to complications in the circulation. Some heart and brain infections may also occur.
The glycemic curve exam
Blood glucose curve examination is performed to determine the presence of type II diabetes. This test was developed because this type of diabetes is often asymptomatic. In other words, the person who has the disease has no symptoms.
Therefore, this test can measure the body’s ability to metabolize glucose. In the case of type II diabetes, for example, this ability is compromised. At the same time, it is also impaired in people who have changes in metabolism related to the assimilation of carbohydrates.
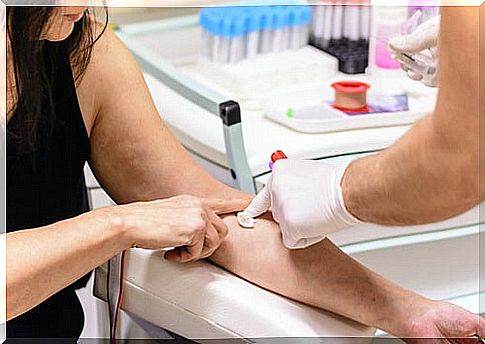
How is the glycemic curve exam performed?
The first thing you should do is take a fasting blood glucose test. The person must do this without having eaten between 8 and 12 hours before the exam.
In the laboratory, a blood sample is taken to determine the concentration of glucose in the blood – blood glucose. Depending on the results, a dose of glucose will be administered orally, dissolved in 250 milliliters of water. This measurement may vary depending on the patient’s body weight.
The rule states that 1.75 grams of glucose should be administered for each kilogram of weight, up to a maximum of 75 grams. Therefore, if a child is going to be tested, the glucose dose will be lower.
After taking the glucose, blood samples will be taken every 30 minutes for the next 2 hours. With the results obtained, a graph will be drawn up expressing the glycemic curve.
Normal Glucose Tolerance Values
The values expressed in blood glucose tests and blood glucose curve are very important to determine the presence or absence of diabetes, as well as the type of disease.
If the glucose content in the blood glucose test is between 60 and 100 mg/dL, the values are considered normal. Likewise, values less than 200 mg/Dl in the first hour and less than 144 mg/Dl in the first two hours are also considered normal.
Abnormal glucose tolerance values
If your fasting blood glucose test is between 100 and 125 mg/dL, it is a sign of prediabetes. The diagnosis is confirmed with a blood glucose concentration between 140 and 199 mg/dL within two hours of glucose ingestion.
Values that indicate type II diabetes
A glucose content greater than 125 mg/dL in the blood glucose test is sufficient to discourage the blood glucose curve test.
If carried out, the person’s life is at risk and may cause hyperglycemic shock.
In turn, a result greater than 200 mg/dL two hours after glucose ingestion indicates type II diabetes.
This is one of the most used tests to determine the presence of type II diabetes mellitus. Regardless of the case, if the test result is unfavorable, the person will need to change their lifestyle. The doctor will indicate how to prepare a proper diet and carry out other activities, if applicable.









